Are you fascinated by the thrill of the stock market and eager to explore opportunities for quick profits? Intraday trading, buying and selling stocks within the same trading day, can be a lucrative venture. But it’s also a high-stakes game that requires knowledge, discipline, and a well-defined strategy.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the essential tools and insights to navigate the exciting world of intraday trading and unlock its profit potential.
What is Intraday Trading?
Intraday trading involves capitalizing on short-term price fluctuations of stocks. Unlike long-term investing, the goal is not to hold assets for extended periods but to make quick profits from small price movements throughout the trading day. All positions are closed before the market closes to avoid overnight risks.
Key characteristics of Intraday Trading:
- Short-term focus: Trades are opened and closed within a single trading day.
- Leverage utilization: Brokers often offer leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with a smaller capital outlay.
- Technical analysis driven: Traders heavily rely on charts, indicators, and patterns to predict price movements.
- High risk, high reward: The potential for quick profits is matched by the risk of rapid losses.
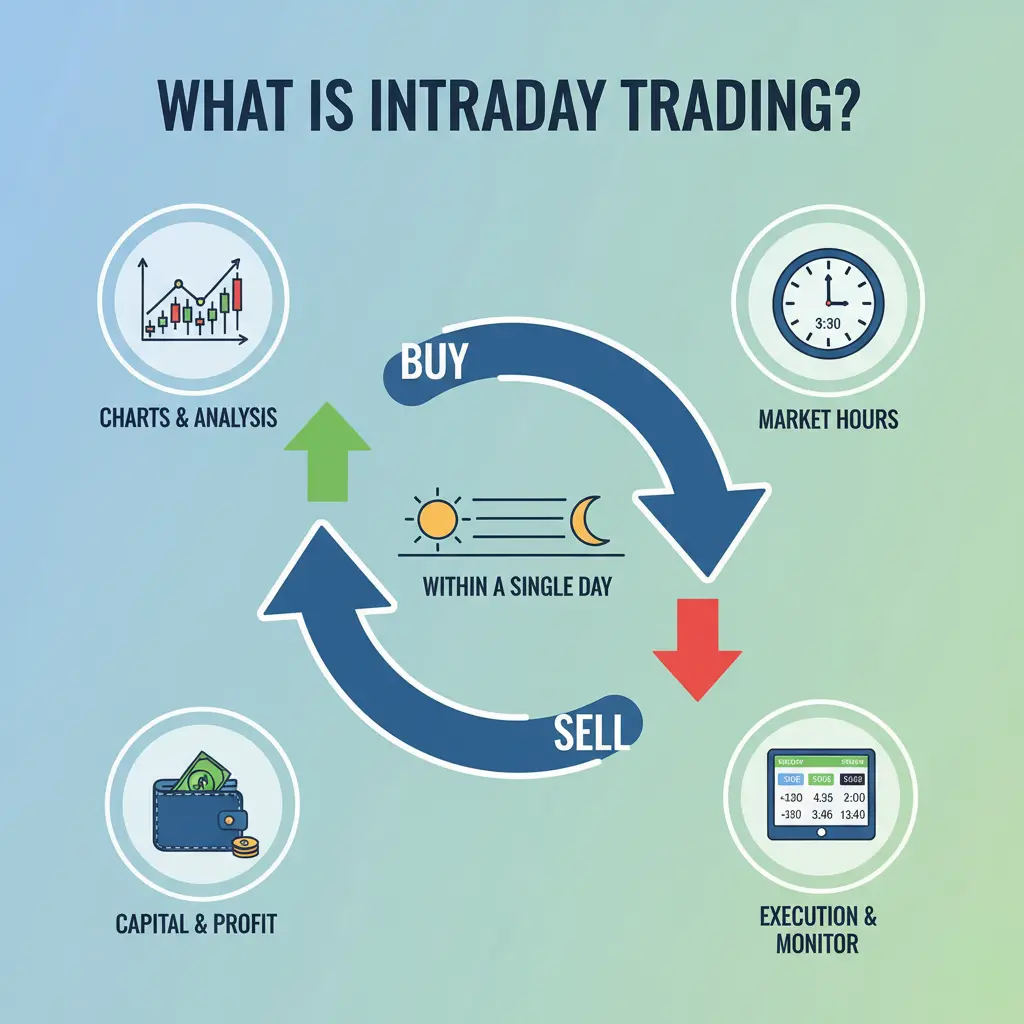
What is Intraday Trading?
- Definition: Buying and selling stocks within the same trading day.
- Goal: Profit from short-term price fluctuations.
- Key Feature: All positions closed before market close.
- Tools: Technical analysis, charts, indicators.
- Risk: High.
- Reward: Potentially High.
Why Choose Intraday Trading?
Intraday trading offers several compelling advantages for those who understand its dynamics:
- Quick Profit Potential: The primary allure is the ability to generate profits within hours, rather than weeks, months, or years.
- No Overnight Risk: Since all positions are squared off by day-end, traders are not exposed to overnight market fluctuations or news events that can drastically impact stock prices.
- Flexibility: With the right setup, you can trade from almost anywhere with an internet connection.
- Leverage Benefits: Brokers provide leverage, meaning you can trade with more capital than you physically possess, amplifying potential returns (and risks).
Essential Strategies for Intraday Trading
Success in intraday trading hinges on a robust strategy. Here are some of the most effective approaches:
- Momentum Trading: This strategy involves identifying stocks with strong price movements in a particular direction. Traders aim to jump on board these trends and exit once the momentum shows signs of slowing.
- Scalping: Scalpers aim to make numerous small profits from tiny price changes throughout the day. This requires rapid execution and a deep understanding of market microstructure.
- Breakout Trading: This involves identifying key support and resistance levels. Traders enter a position when the stock price “breaks out” above resistance or “breaks down” below support, expecting a sustained move in that direction.
- Reversal Trading: Contrary to momentum trading, reversal traders look for instances where an existing trend is likely to change direction. This often involves identifying overbought or oversold conditions.
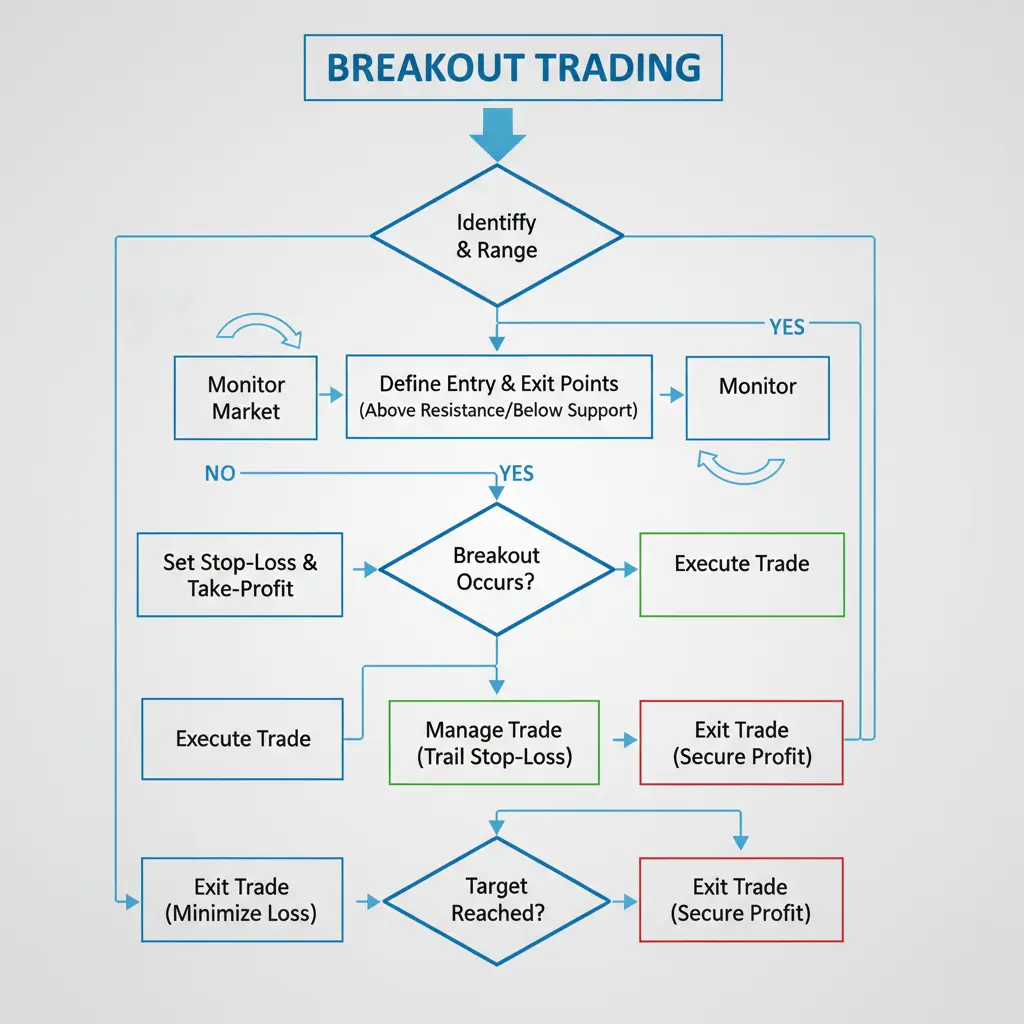
Breakout Trading Strategy
- Identify Key Levels: Find clear Support and Resistance lines on charts.
- Monitor Price: Watch for price approaching these levels.
- Wait for Breakout: Look for a decisive move through Support or Resistance.
- Enter Trade: Open a position in the direction of the breakout.
- Set Stop Loss: Place a stop-loss order just inside the broken level to limit risk.
- Take Profit: Exit the trade when the price shows signs of losing momentum or reaches a target.
Key Factors for Profitable Intraday Trading
To consistently make profits, several factors must be meticulously considered:
- Market Volatility: Intraday traders thrive on volatility. High-volatility stocks offer more significant price movements, creating better profit opportunities.
- Liquidity: Always trade highly liquid stocks. This ensures you can enter and exit positions quickly without significantly impacting the price. Low-liquidity stocks can lead to slippage and difficulty in executing trades.
- Technical Analysis: Mastering technical analysis is non-negotiable. Learn to read charts, understand indicators (like RSI, MACD, Moving Averages), and identify chart patterns (like head and shoulders, triangles).
- Fact: A study published in the Journal of Finance found that technical analysis, when applied systematically, can offer statistically significant predictive power in certain market conditions (Source: Lo, A. W., Mamaysky, H., & Wang, J. (2000). Foundations of Technical Analysis: Computational Algorithms, Statistical Inference, and Empirical Implementation. The Journal of Finance, 55(4), 1705-1765).
- Risk Management: This is arguably the most crucial aspect.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Always place a stop-loss order to limit potential losses on a trade. Never trade without one.
- Position Sizing: Determine how much capital to allocate to each trade based on your risk tolerance. A common rule is to risk no more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on any single trade.
- Diversification (within intraday context): While you’re not diversifying a long-term portfolio, avoid putting all your capital into a single, highly speculative intraday trade.
- Trading Psychology: Emotions can be a trader’s worst enemy.
- Discipline: Stick to your trading plan and avoid impulsive decisions.
- Patience: Wait for the right setups; don’t force trades.
- Emotional Control: Don’t let fear or greed dictate your trading decisions.
- Economic News & Events: While intraday trading is short-term, significant economic news releases (e.g., interest rate decisions, inflation reports, corporate earnings) can trigger immediate and dramatic price movements. Be aware of the economic calendar.
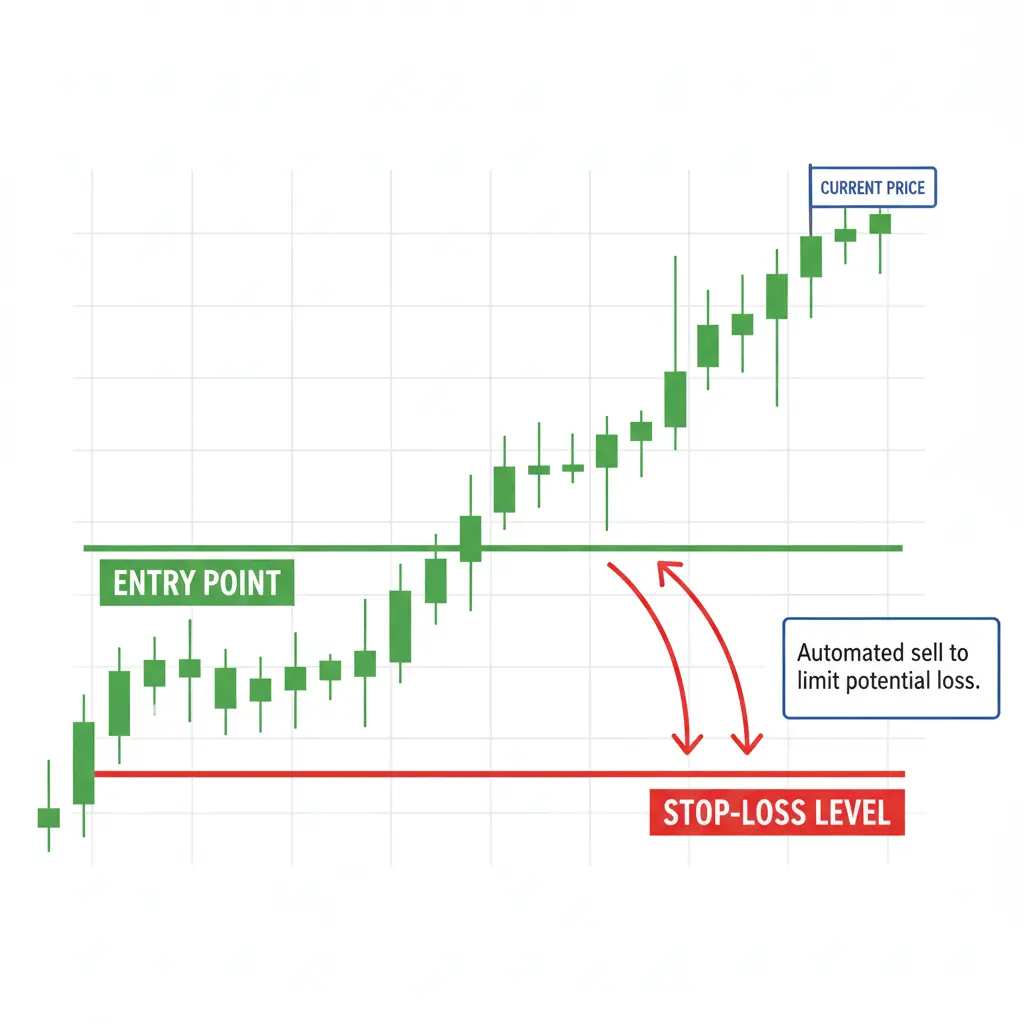
Understanding Stop-Loss Orders
- Entry Price: $100.00
- Current Price: $100.50
- Stop-Loss Price: $99.00
- Purpose: Automatically sell if the price drops to $99.00, limiting potential loss to $1.00 per share.
- Why use it? Protects capital, enforces discipline, manages risk.
- Rule: NEVER trade without a stop-loss!
Setting Up Your Intraday Trading Account
Getting started requires a few practical steps:
- Choose a Reputable Broker: Select a broker with low commissions, a reliable trading platform, good customer service, and access to the markets you wish to trade.
- Open a Demat and Trading Account: These are essential for holding shares electronically and executing trades.
- Fund Your Account: Start with capital you are comfortable losing. Never trade with money you cannot afford to lose.
- Understand Your Platform: Familiarize yourself with your broker’s trading platform, its features, charting tools, and order types.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even experienced traders make mistakes. Here are some common pitfalls to steer clear of:
- Overtrading: Entering too many trades, often out of boredom or a desire to “make up” for losses.
- Lack of a Trading Plan: Trading without a defined strategy, entry/exit points, and risk management rules is a recipe for disaster.
- Emotional Trading: Allowing fear of missing out (FOMO) or revenge trading after a loss to influence decisions.
- Ignoring Stop-Loss Orders: The most common and costly mistake. Holding onto a losing trade in hopes it will rebound.
- High Leverage without Understanding Risk: While leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies losses.
- Trading Illiquid Stocks: Getting stuck in a position because there are no buyers or sellers.
The Power of Practice: Paper Trading
Before risking real money, engage in paper trading (also known as virtual trading or simulated trading). Most brokers offer this feature.
- Benefits:
- Test strategies in a real-time market environment without financial risk.
- Familiarize yourself with the trading platform.
- Develop discipline and emotional control.
- Refine your understanding of technical analysis.
Fact: Research from the University of California, Berkeley suggests that deliberate practice, even in simulated environments, significantly improves skill acquisition in complex tasks like trading (Source: Ericsson, K. A., Krampe, R. T., & Tesch-Römer, C. (1993). The role of deliberate practice in the acquisition of expert performance. Psychological Review, 100(3), 363).
Conclusion: Discipline is Your Greatest Asset
Intraday trading can be a highly profitable endeavor, offering the potential for significant daily gains. However, it demands unwavering discipline, continuous learning, and robust risk management. Arm yourself with knowledge, practice diligently, and always prioritize protecting your capital. With a well-thought-out plan and emotional control, you can navigate the exciting world of intraday trading and carve out your path to financial success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is the minimum capital required for intraday trading?
A1: While you can start with a few thousand dollars, it’s generally recommended to have at least $500 to $1,000 for meaningful position sizing, especially considering transaction costs and potential losses. Regulations vary by country and broker.
Q2: Is intraday trading suitable for beginners?
A2: Intraday trading is advanced and high-risk. Beginners should start with thorough education, extensive paper trading, and small capital amounts. Long-term investing is often recommended for absolute beginners.
Q3: How much profit can I expect from intraday trading?
A3: Profit potential varies wildly based on capital, skill, market conditions, and strategy. There’s no fixed answer, and it’s important to have realistic expectations. Focus on consistent, small gains rather than large, infrequent ones.
Q4: What are the best indicators for intraday trading?
A4: Popular indicators include Moving Averages (MA), Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Bollinger Bands. However, no single indicator is perfect; combining them and understanding their context is key.
Q5: What is the ideal time frame for intraday charts?
A5: Most intraday traders use multiple time frames. Common choices include 1-minute, 5-minute, 15-minute, and 30-minute charts for entry/exit decisions, combined with hourly or daily charts for overall trend analysis.
About the Author
Tanishq Mittal is a passionate financial markets enthusiast and a seasoned trader with 5+ years of experience navigating the dynamic world of stocks. With a background in finance. He specializes in technical analysis and risk management strategies. He believes in empowering individuals with the knowledge and tools to make informed trading decisions and aims to demystify complex market concepts for a broader audience. Through insightful articles and practical advice, He is dedicated to helping aspiring traders achieve their financial goals.

